Visual Studio 2022 - Remote Testing
Several months ago I wrote a blog post explaining how could we debug a unit test running in a Linux container using Visual Studio 2019. In that post I mentioned that the experience is far from being great in VS2019. It was possible, but it required some manual steps.
When we want to debug a unit test running in a Linux container, our expectation is to have the same experience as when debugging locally:
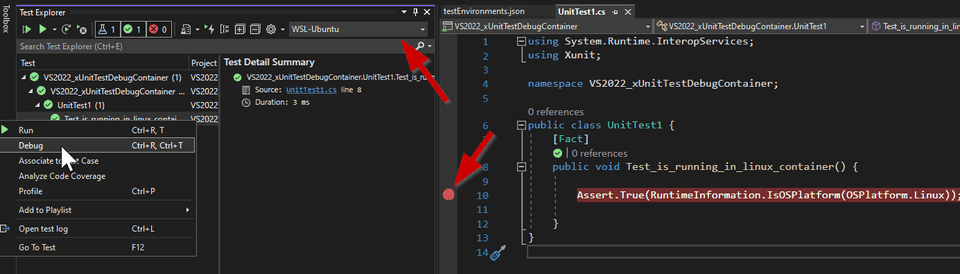
- Go to Test Explorer
- Right Click on the Test and select Debug
- The debugger starts and stops in a breakpoint inside the test
That’s exactly what Visual Studio 2022 brought to us with Remote Testing. Let’s see how it works.
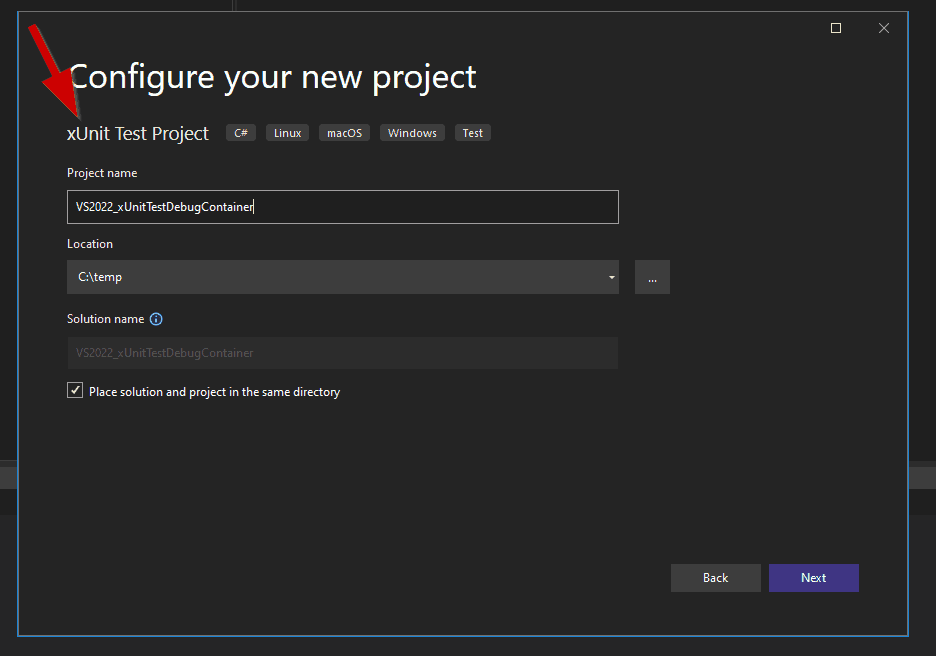
Create a xUnit test project.
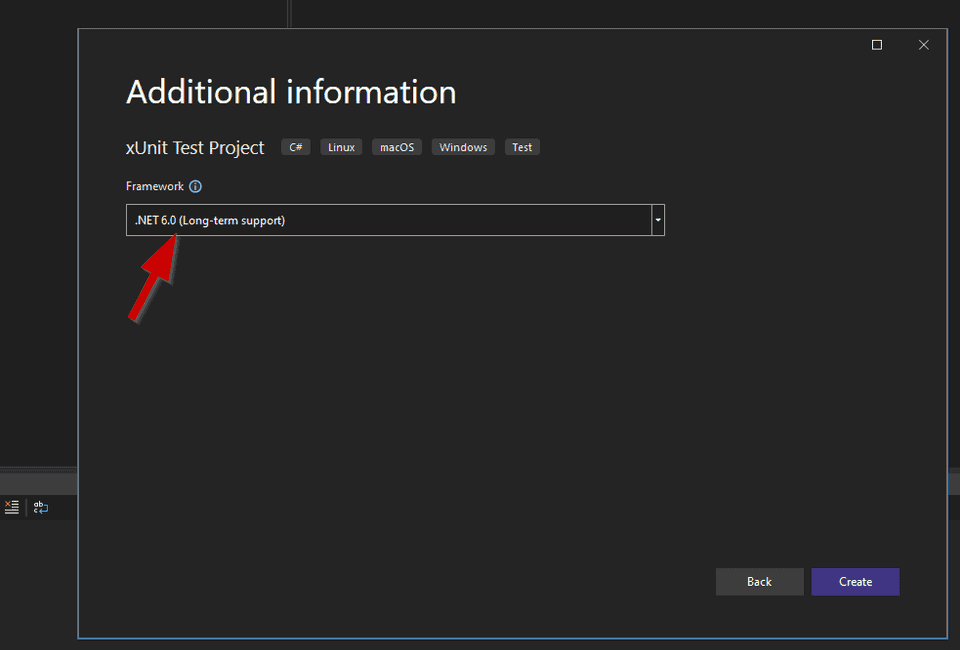
Choose .NET 6.0
For demonstrating purposes, let’s create the same test used when demonstrating how to debug in Visual Studio 2019. This is a simple test that asserts that the test is running in a Linux container.
[Fact]
public void Test_is_running_in_linux_container() {
Assert.True(RuntimeInformation.IsOSPlatform(OSPlatform.Linux));
}Now add a new file testEnvironments.json to the root of the solution
{
"version": "1", // value must be 1
"environments": [
{
"name": "WSL-Ubuntu",
"type": "wsl",
"wslDistribution": "Ubuntu-20.04"
}
]
}Basically I am adding a new test environment to run my tests in a WSL Ubuntu
20.04 distribution. To check the list of distributions you can run wsl
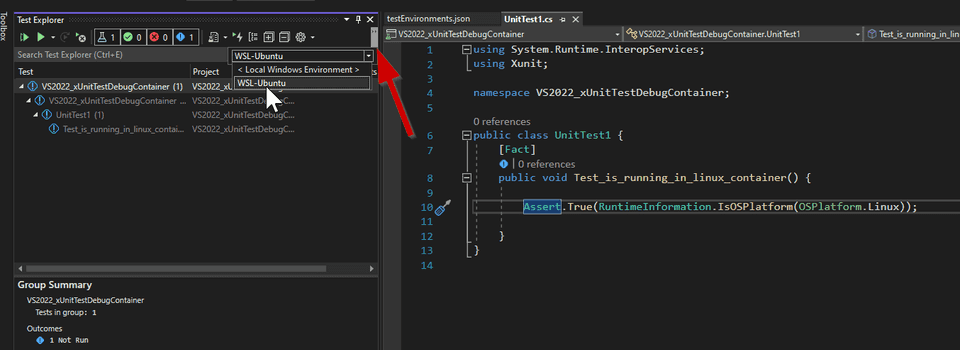
--list in a command prompt. In Test Explorer you now have a dropdown with the
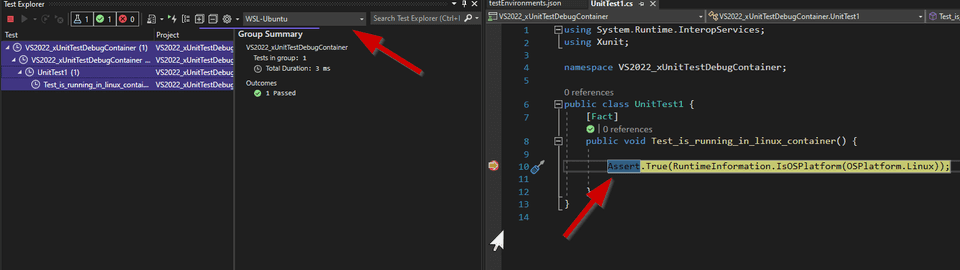
list of test environments. Let’s select the test environment just added,
WSL-Ubuntu.
Note: if you don’t see the new environment, then close Visual Studio and launch it again. This is an experimental feature and I have experienced some issues while playing with it. We could also add environments connected to docker containers running locally on Docker Desktop, or even remote environments connected by SSH.
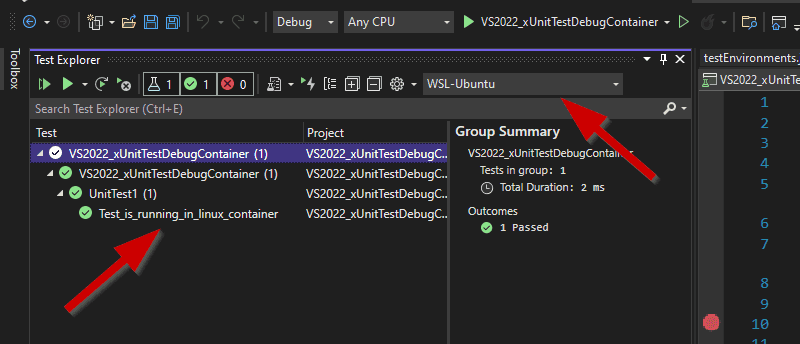
Put a breakpoint in the test that you want to debug and select it in Test Explorer to start debugging it.
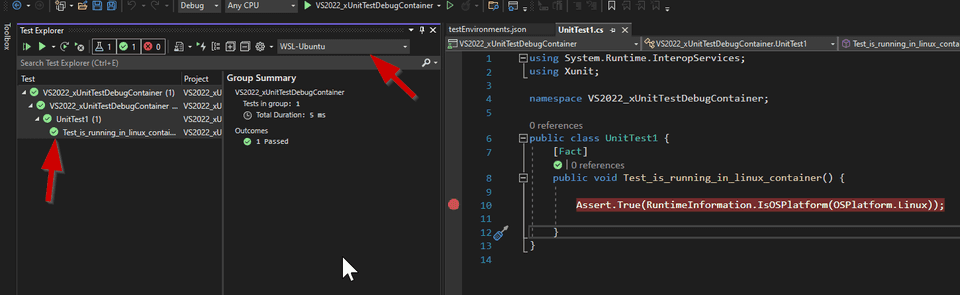
Debugger stops at the breakpoint
And the test passes.
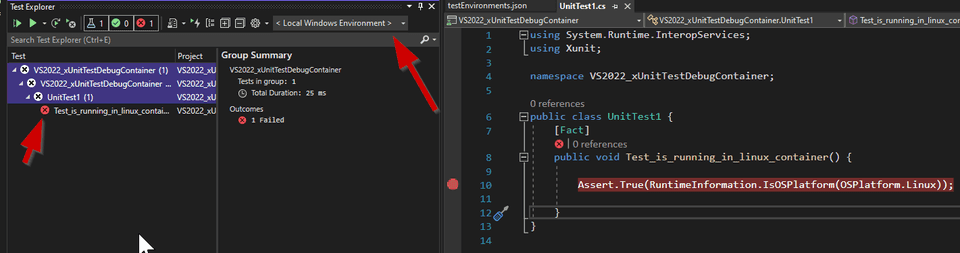
Change the environment to < Local Windows Environment > and you will see that
the test fails.
Thank you Visual Studio 2022 for greatly simplify this experience of remote testing.