VS 2019 on Windows - Debugging a unit test running in a Linux container
Docker Support in Visual Studio 2019 is great, providing a great experience for running and debugging ASP.NET and Console applications in docker containers. But when it comes to Unit Test projects the experience is not so great.
My expectation was that the experience of running or debugging unit tests in containers would be exactly the same as ASP.NET or Console apps. I was even expecting that I could use the VS Test Explorer: as long as the Docker launch profile was selected, I thought that the tests would be running/debugging inside the container. Unfortunately it’s not the case.
So, imagine that you are working with Visual Studio 2019 on Windows, building a .NET Core project that would be deployed in Windows, but also in Linux, and a specific test is failing in Linux, and you want to debug it. How can we do it in a simple way?
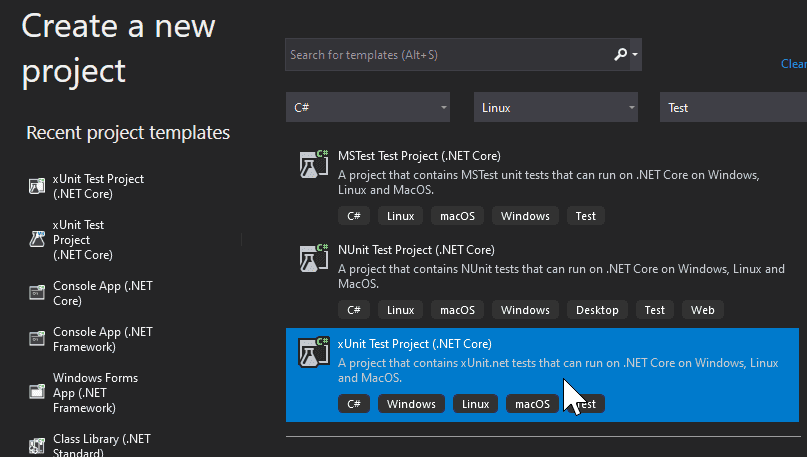
Let’s create a xUnit (my test framework of choice) test project.
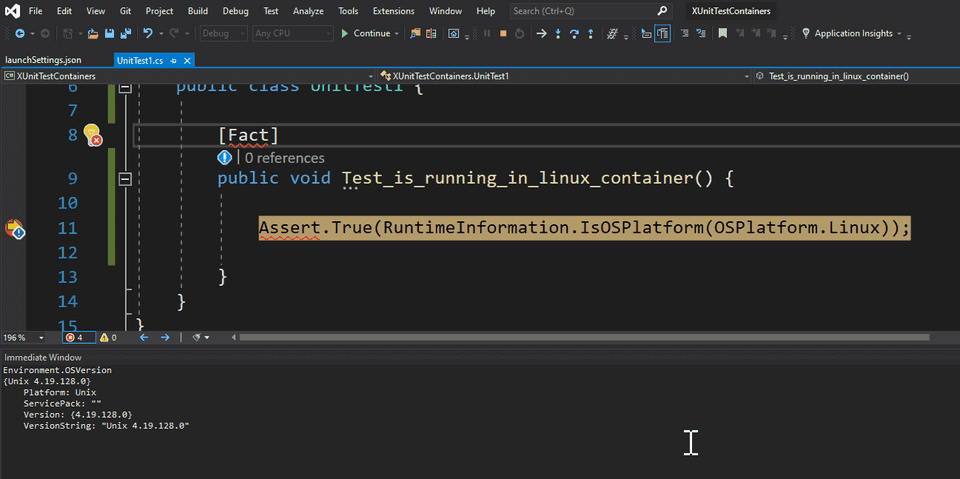
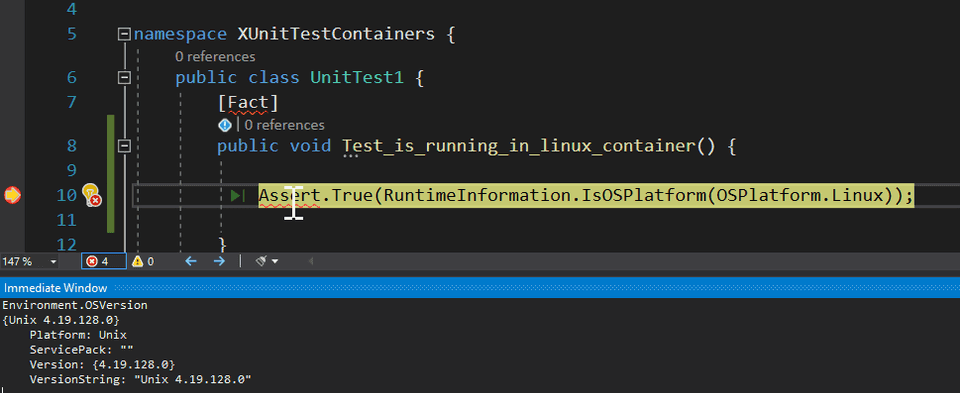
For demonstrating purposes, let’s create a simple test that asserts that the test is running in a Linux container.
[Fact]
public void Test_is_running_in_linux_container() {
Assert.True(RuntimeInformation.IsOSPlatform(OSPlatform.Linux);
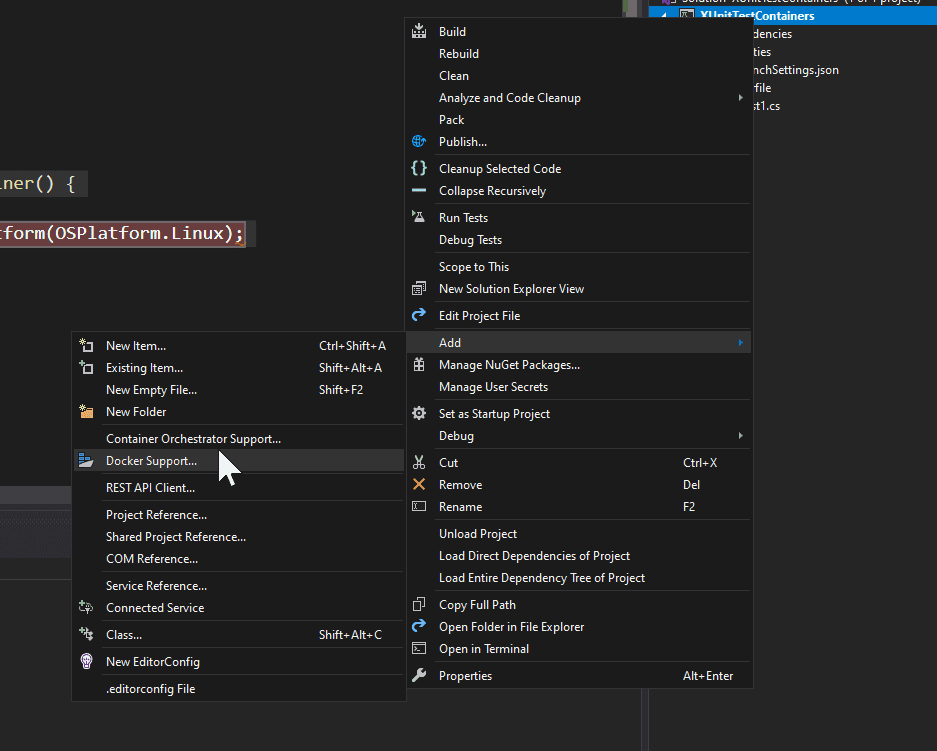
}Unlike ASP.NET projects, in Unit Test projects we don’t have the option “Enable Docker Support” while creating the project. Though, the option is still available via Solution Explorer. Let’s try it.
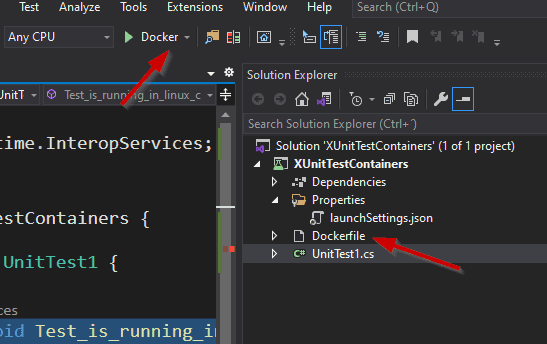
Choose Linux as target. The result: a Dockerfile is added to the solution and
a new Docker launch profile is added to the list of profiles.
This is exactly the same behavior we get in an ASP.NET or Console project. However, the running experience is not the same: the integration between the test explorer and the docker container does not work.
That’s what have triggered me to do some investigation. First we need to
understand what VS is doing when we start debugging in a container with the
the Docker profile selected.
VS optimizes the Debug experience by using the so called Fast build
mode.
In this mode, the docker build command used by VS only uses the base stage
of the Dockerfile. Furthermore, when selecting the Docker profile a
Project warmup is triggered consisting in the following steps:
- Check Docker Desktop is running and is set to the same operating system as project
- Pull the image in the first stage (the
basestage) - Build the
Dockerfileand start the container
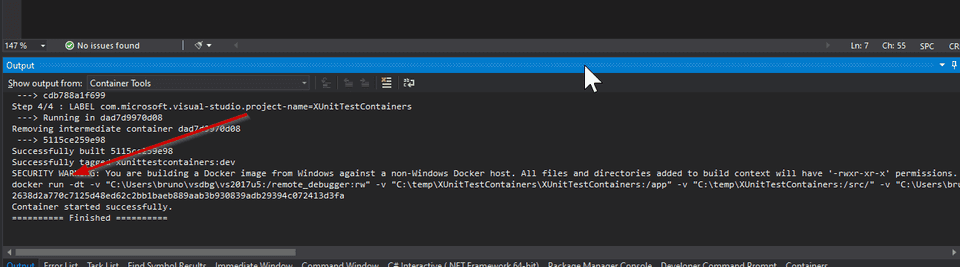
When VS starts the container, some volume mappings are created for the remote
debugger, and for Nuget folders. You can check the full docker run command in
the Containers Tools output window.
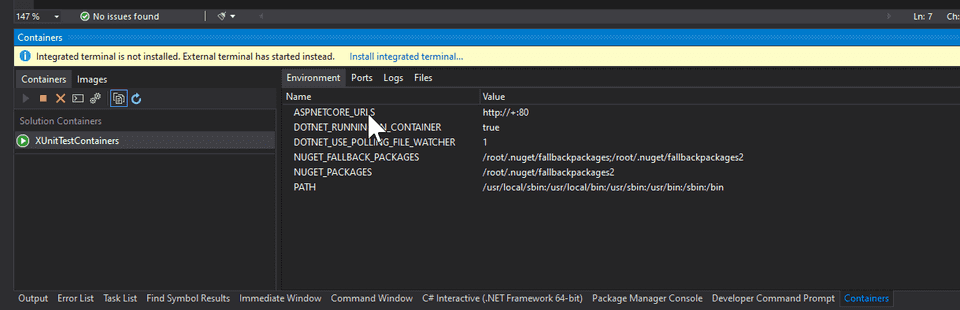
The container is now running. We can check it in the Containers window.
Now we want to run our tests inside the container. Basically we just need to run
the dotnet test command inside the container. We can do it using the docker
exec command.
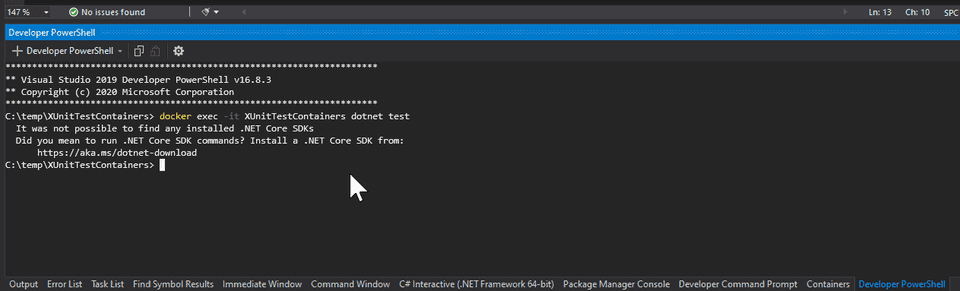
docker exec -it <name_of_the_container> dotnet testLet’s see what happens.
We got the following error
It was not possible to find any installed .NET Core SDKs
Now we need to look at the Dockerfile to understand what image is running.
This the Dockerfile originally generated by VS.
#See https://aka.ms/containerfastmode to understand how Visual Studio uses this Dockerfile to build your images for faster debugging.
FROM mcr.microsoft.com/dotnet/core/runtime:3.1-buster-slim AS base
WORKDIR /app
FROM mcr.microsoft.com/dotnet/core/sdk:3.1-buster AS build
WORKDIR /src
COPY ["XUnitTestContainers/XUnitTestContainers.csproj", "XUnitTestContainers/"]
RUN dotnet restore "XUnitTestContainers/XUnitTestContainers.csproj"
COPY . .
WORKDIR "/src/XUnitTestContainers"
RUN dotnet build "XUnitTestContainers.csproj" -c Release -o /app/build
FROM build AS publish
RUN dotnet publish "XUnitTestContainers.csproj" -c Release -o /app/publish
FROM base AS final
WORKDIR /app
COPY /app/publish .
ENTRYPOINT ["dotnet", "XUnitTestContainers.dll"]The first thing to notice is the comment at the top of the file. Follow that
link to understand the Fast build mode I mentioned earlier. In the Fast mode,
only the base stage is used. In this case the base stage is using a
runtime image which does not include the .NET SDK required to run tests. We
need to change our Dockerfile to use a .NET SDK image in the base stage. We
can also remove all the other stages since they are not being used when
debugging.
#See https://aka.ms/containerfastmode to understand how Visual Studio uses this Dockerfile to build your images for faster debugging.
FROM mcr.microsoft.com/dotnet/core/sdk:3.1-buster AS base
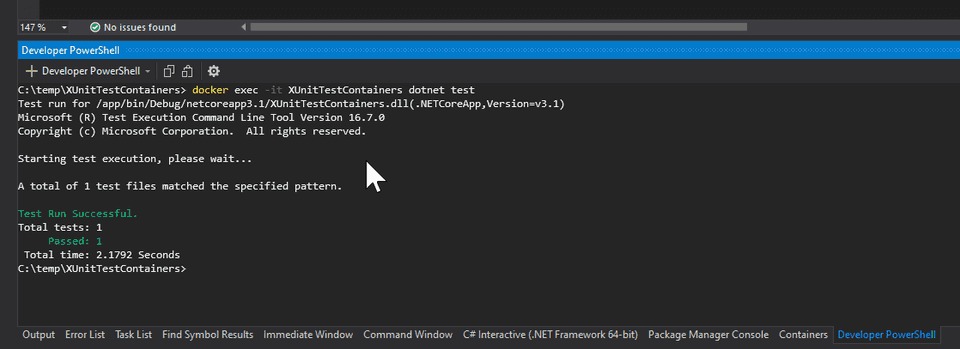
WORKDIR /appRebuild the solution. And let’s try again to run the dotnet test command.
Great, we are now running our tests inside the container. Now we just need to have a way to launch the remote debugger and attach to the process responsible to run the tests.
When we run a dotnet test command, a new process is started to run
vstest.console to execute the tests, which in turn runs the testhost.dll. We
can instruct testhost to pause execution waiting for a debugger to be
attached, by using an environment variable VSTEST_HOST_DEBUG=1. Let’s run
the same docker exec command passing this environment variable.
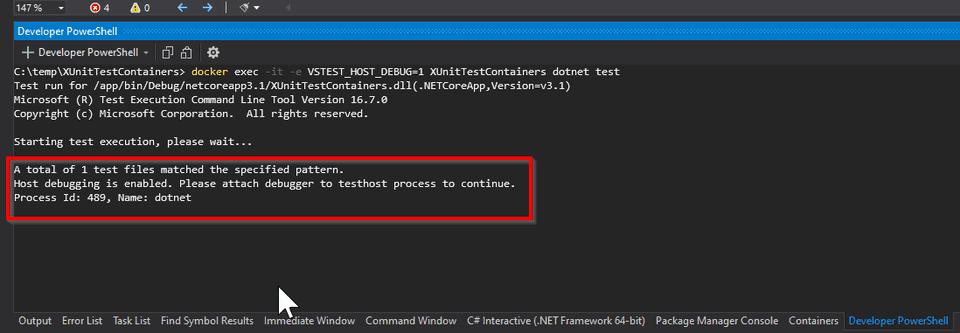
docker exec -it -e VSTEST_HOST_DEBUG=1 <name_of_container> dotnet testWe got the following info
_A total of 1 test files matched the specified pattern. Host debugging is
enabled. Please attach debugger to testhost process to continue. Process Id: 643, Name: dotnet_
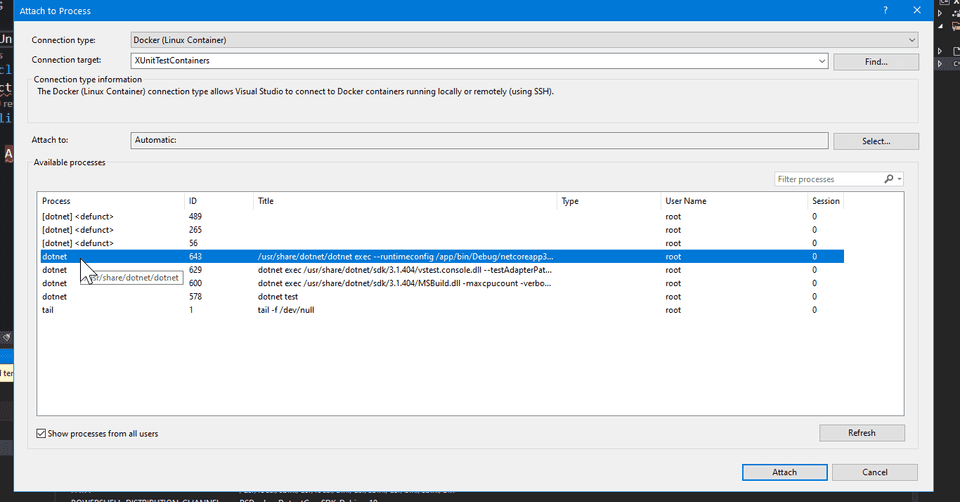
Now we just need to attach the debugger to the testhost process, which in
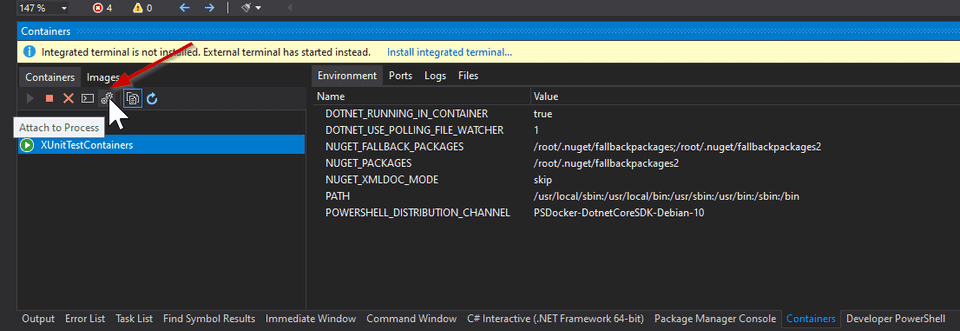
this case has its PID=643. Let’s use the Container window to attach the debugger
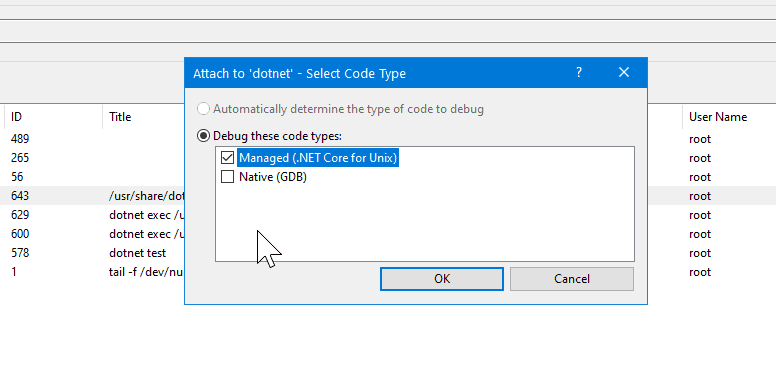
to this process.
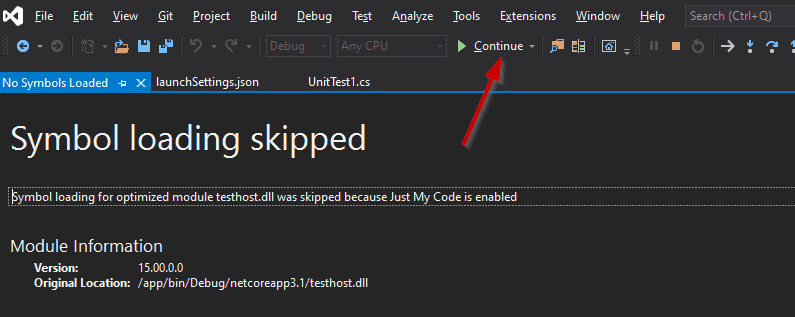
Wait a few seconds. You may see a screen informing that symbol loading was
skipped for testhost.dll.
Just click Continue and your breakpoint is hit.
You can now debug your test inside the Linux container. The whole debugging unit tests experience is not ideal and I truly hope VS integrates Test Explorer with Containers Tools very soon.